Sustainability
How Microhubs Contribute Towards Sustainable Urban Freight Logistics
May 12, 2021
9 mins read

Due to the ripple effects caused by the Covid-19 pandemic, e-commerce businesses are reworking their urban deliveries. Densely populated cities pose a logistical challenge to delivery businesses. A growing number of vehicles lead to congestion, air pollution and noise, thereby reducing the quality of life.
Last-mile delivery determines urban economic competitiveness. Urban logistics has numerous complexities with diverse levers and multiple stakeholders.
- Local authorities want to reduce noise and congestion
- Transportation companies and retailers want to control their costs while maintaining their service levels.
Logistics businesses find it challenging to balance their efficiency standards with rising costs. A major hindrance for their last-mile delivery success is the logistics sprawl.
What is a Logistics Sprawl?
Logistics sprawl is the concentration of logistics facilities in peripheral regions of metropolitan areas over time. It is either caused by skyrocketing land prices in urban areas, increase in population density or space availability in urban outskirts.
Logistics sprawl causes increased travel time and impacts delivery reliability. It increases fuel consumption, thereby leading to congestion and increased transportation costs. Diversified urban logistics spaces like microhubs is a good cost-saver for logistics businesses to counter this logistics sprawl.
Types of Urban Logistics Spaces
Urban Logistics spaces are categorized into four types based on their closeness to delivery location and footprint size. They are
- Suburban Warehouse
- Urban Consolidation Centres
- Micro hubs
- Lockers

What is a Microhub?
Microhub is a micro-consolidation logistics facility set near a final delivery point (within 1 to 5 km from the final destination). They are also called micro-fulfillment centers, delivery microhubs or micro-distribution hubs. It is a type of urban logistics space that links suburban warehouses to final delivery points.
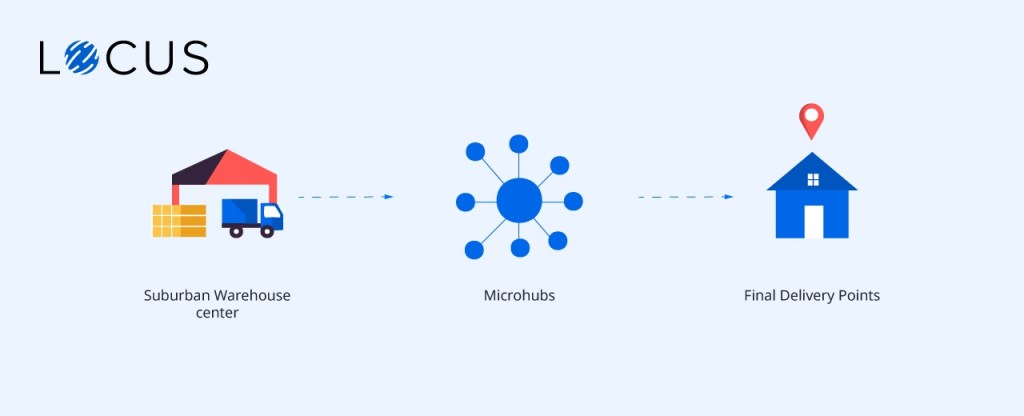
Microhubs have smaller physical footprints that range from 1,000 square feet to 10,000 square feet. They are a form of Urban Consolidation Center (UCC) that can be operated on a temporary or permanent basis by one or more businesses.
Microhubs facilitate eco-friendly delivery options like drones, robots, cargo bikes, or automated vehicles. They are beneficial for industrial parks, campuses, business parks, hospitals etc.
How are Urban Consolidation Centers different from Microhubs?
A UCC is located within the city’s suburbs or borders where goods coming from outside the city can be consolidated. It serves an urban area and has a relatively large physical footprint from 500,000 square feet to 5 million square feet. They are the most common consolidation schemes in city logistics.
Many shipping companies like Amazon are reclaiming formerly abandoned spaces such as parking garages, railyards or shopping malls to nudge distribution centers close to consumers’ doorsteps.
Characteristics of Microhub Operations
- They focus on the delivery of lighter and smaller loads
- They aim to reduce the number of vehicle trips in urban areas
- They focus on eco-friendly transport like electric vehicles, cycling or walking for the last-mile delivery
- They are owned and operated by private transportation companies
- Their facilities are located within an urban area near-final delivery point
Key Elements for Success of Microhubs operations
- A quantified estimate of the number of potentially participating carriers is necessary during every stage
- It should serve areas where delivery activities are difficult due to limited access to streets, restricted traffic conditions, or limited curb space for large vehicles.
- Microhub operations should be functional in high-density areas where high-volumes of delivery accumulate.
- In the case of multi-carrier practices, strong cooperation and trust among partner carriers is necessary.
How do microhubs help businesses achieve EcoLogistics principles for last-mile delivery?

Globally, cities ‘account for 60 to 80 percent of energy consumption and at least 70 percent of carbon emissions’. – UNDP, 2019.
Increasing energy consumption in urban areas has contributed to mass carbon emissions. This has forced global logistics experts to build EcoLogistics principles. EcoLogistics principles are the foundational sustainable principles for moving goods in urban areas. They are:
- Using alternative delivery options
- Safe urban delivery vehicles for safe streets
- Including land use planning for freight delivery
- Building consolidation strategies for urban deliveries
- Making delivery operations optimal
- Creating multi-stakeholder decision-making structures
- Build frameworks for climate-friendly business models
- Encourage the future developments of sustainable logistics
EcoLogistics principles help local authorities create resource-efficient urban goods distribution systems. It is necessary for sustainable transportation and more livable communities. Here are the ways microhubs help businesses to achieve EcoLogistics principles.
Improves efficiency in delivery operations
There is more pressure on delivery operations, as customers increasingly demand same-day delivery and next-day delivery. Due to rising parcel volumes, unexpected delivery delays are inevitable in crowded cities. Microhubs enable logistics carriers to make on-time deliveries without any peak-hour pressures.
Microhubs make it easier to match the pickups and deliveries for vehicles. It helps drivers deliver small loads with greater frequency using eco-friendly vehicles. As micro-distribution centers are closer to delivery locations, they reduce fuel consumption by eliminating idling costs.
Faster order deliveries
The COVID-19 pandemic has reduced customer preferences for fast delivery. Though customers have become lenient on fast delivery, they are expecting businesses to fulfill their on-time delivery promises. A longer distance between warehouses and the final delivery point can impact on-time deliveries.
Last-mile expenses account for 28% of total transportation costs and are increasing every passing year. Managing last-mile delivery cost is essential for businesses to foster brand loyalty.
Being closer to final delivery points, microhubs reduce the distance travelled in the last-mile. Faster deliveries in crowded areas improve on-time delivery rates of businesses, making last-mile logistics cost-effective.
Creates deeper insights into deliveries
Microhubs help logistics businesses hold more product volume per square feet than in traditional warehouses. Beyond fulfilling orders faster, it helps businesses gather localized data on customers like brand preferences or order size. These insights help businesses plan their budgets for last-mile deliveries.
Microhubs give logistics companies a microscopic view of their delivery performance in different urban delivery zones. It helps logistics managers to design plans that are well-suited for different delivery zones. These customized plans help them upsize or downsize the fleet based on customer demand, thereby enhancing flexibility.
Enhances customer experience
We are still in the pandemic stage and logistics businesses are striving to improve their customer experience. Businesses that offer their customers a fast, convenient, safe and low-cost delivery survive in the market.
The quality of last-mile delivery is determined by speed and agility. Setting up microhubs reduces the vehicle kilometers traveled per delivery as delivery locations are closer. This minimizes longer wait times and cuts down shipping costs.
With quicker deliveries and cheaper order fulfillment, microhubs help businesses eliminate failed deliveries. This enables them to provide a delightful delivery experience through frictionless deliveries.
Challenges in setting and operating microhubs
Lack of order preparation capacity
If a micro-fulfillment facility is located within a store, it becomes difficult to combine orders without affecting inventory in brick and mortar stores. This makes it impossible to prepare a large number of orders compared to distribution centers.
Lack of storage capacity
Though many businesses practice space optimization, urban centers do not have a lot of storage surface area. Densely populated urban areas have a high demand for storage space, hence the cost to own them or lease them is very high. Without the rightly-spaced and rightly-sized storage area, it is difficult to serve a densely populated customer base.
Difficulty to accommodate additional demand
An increase in demand from online shoppers can add burden to the parcel carrier company. Peak online shopping seasons require a large storage capacity for goods.
Though microhubs facilitate quick delivery of parcels, there are chances for goods to quickly accumulate during peak delivery seasons. Allowing these goods to stay there increases idle storage costs.
Conclusion
With the global freight demand expected to triple, the future of urban freight logistics depends on how businesses execute microhubs in their delivery networks.
Delivery logistics software from Locus makes your delivery operations in microhubs smoother. It helps parcel carriers plan their routes better and reduce fuel consumption delivery costs. It also helps them easily track, coordinate and make on-time deliveries in dense urban areas with the available resources.
Make your delivery microhubs efficient with our product offerings!

Infographic by Locus
Share this infographic by using this embed code:
<a href="https://locus.sh/resources/build-an-efficient-urban-logistics-with-microhubs/" target="_blank" style="text-align: center; display: block;">
<img src="https://locus.sh/assets/img/infographic/resources/build-an-efficient-urban-logistics-with-microhubs.jpg" alt="Build an Efficient Urban Logistics with Microhubs" style="width:100%;height:auto;max-width:750px;margin:auto;"></a><br/>Infographic by <a href="https://locus.sh/">Locus</a>References
- https://population.un.org/wup/Publications/Files/WUP2018-Report.pdf
- https://www.adlittle.com/sites/default/files/viewpoints/adl_the_future_of_urban_mobility_report.pdf
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340800857_Investigating_the_use_of_microhubs_and_crowdshipping_for_last_mile_delivery
- https://wrirosscities.org/sites/default/files/enhancing-ndcs-opportunities-transport.pdf
- https://reports.valuates.com/market-reports/QYRE-Auto-22T543/global-last-mile-delivery
- https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/transport/itf-transport-outlook-2019/summary/english_c013afc7-en;jsessionid=4ivY38MSN0ObBuni75PytTG3.ip-10-240-5-189
Related Tags:

Retail & CPG
Convenience is King: Here’s Why the Click-and-Collect Model Works
The days of scanning through shelves in a grocery store for your favorite brand of mustard are long gone. This means no more standing in long queues, no more trolley bumping, and no store assistants trailing behind you. The obvious alternative may seem home delivery. But that also means additional shipping costs and a tedious […]
Read more
Last Mile Delivery Optimization
How Delivery Logistics Software Improves On-Time In Full (OTIF) Delivery Score
Amongst shippers, 51% told us that a lack of clarity on customer demand was the biggest bottleneck emerging as a result of COVID-19. – Emerging out of the Pandemic Supply Chain Report, Reuters Events, Oct 2020 The ability to fulfill customer needs, by delivering goods at the right place and time, determines the efficiency of […]
Read moreMOST POPULAR
EDITOR’S PICKS
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Stay up to date with the latest marketing, sales, and service tips and news


How Microhubs Contribute Towards Sustainable Urban Freight Logistics